kato-Special Features
EVOLUTION
02
of the TGV and the European high-speed rail network
Specifications of the TGV Sud-Est

The first-generation TGV train was introduced in 1981 alongside the opening of the LGV Sud-Est line. During high-speed tests, it reached 380 km/h, helping to establish the “TGV” name worldwide.
Its distinctive wedge-shaped front design maximizes aerodynamic performance.
The couplers are housed within covers, a mechanism that was later inherited by subsequent TGV trains. When first introduced, the covers bore the 'SNCF' logo. This is a distinctive feature of the Sud-Est trains not seen on other TGV models.
Articulated bogies were adopted between each passenger car, although coil springs were used initially. Later, to improve ride comfort, the springs on the passenger car side were changed to air springs.
The pantograph is equipped with two units for DC and AC. The one on the cab side is for DC, and the one on the passenger car side is for AC. On DC sections, both pantographs on the front and rear locomotives are used, but on AC sections, only the one on the rear locomotive is used.

※Reference image of a different train car

The driver's cab features a circular handle in the center, which functions as both the throttle and brake control. This is a distinctive design feature that differs significantly from the specifications of Japan’s Shinkansen.
※Reference image of a different train car

Extra!
TGV Lesson 1:
“Mastering TGV identification”
Figure out the specific train using multiplication!
Since the debut of the TGV Sud-Est, many high-speed TGV trains have been developed as a result of network expansion and speed improvements.
Although it may seem complicated at first glance, you can distinguish most types to some extent by the combination of:
•Livery / Paint scheme (which reveals the generation/era of the train)
•Lead Car Type = the shape of the locomotives at both ends
•Passenger car type (i.e. single-deck or double-deck)

Livery
Paint Scheme
Lead Car
Types
Passenger Car
Types




Orange
※Only used on the Sud-Est
.jpg)
Reseau
※12-car version=Atlantique

Sud-Est


Single-deck

Silver Blue


(Duplex)


Double-deck
Carmillon
POS
The TGV Family
Manufactured:1988~
TGV Atlantique (TGV-A)
The second-generation TGV train was introduced to coincide with the opening of the LGV Atlantique line. While inheriting the design of the first generation, it features many performance improvements and is the only TGV trainset with 12 cars.
It resembles the Sud-Est model but can be distinguished by its smoothly connected front nose extending from the forehead to the front face.


On 18th May 1990, a test run using train set No. 325 recorded a speed of 515.3 km/h, demonstrating the technological capabilities of French high-speed rail to the world.
Manufactured:1992~
TGV Reseau (TGV-R)
The exterior is the same as the earlier TGV-A, but it was introduced as a more versatile 10-car formation, designed to be usable on any line.
The name “Reseau” means “network” in French, and true to its name, it plays a wide-ranging role, including boosting capacity on the LGV Sud-Est and LGV Atlantique lines, as well as operating as an international train.

Manufactured:1995~

TGV Duplex (TGV-D)
The TGV-D is an all double-deck train developed to significantly increase capacity on the LGV Sud-Est line in response to the surge in business travel demand between Paris and Lyon which occurred after the TGV began operating.
The locomotive design was refreshed with a more rounded appearance. The name "Duplex" refers to its double-deck configuration.

Manufactured:2001~
TGV Reseau Duplex (TGV-RD)
This formation combines TGV-R type locomotives with Duplex (double-deck) intermediate cars and is called the TGV-RD formation (Reseau Duplex).
This formation is mainly seen on the LGV Sud-Est and LGV Méditerranée lines.
〈Additional Information〉
Currently, the train has been reconfigured with single-deck cars and is operating as the TGV-R.
Manufactured:2006~
TGV POS
The TGV-POS began service in 2006, coinciding with the opening of the LGV East Europe line. The train’s design is similar to the earlier TGV-D model, but it is equipped for tri-current operation to enable running into Germany and Switzerland.

〈Additional Information〉
Currently, due to increased demand, double-deck passenger cars that were used in the TGV-RD have been coupled, and the train is operating as the TGV P-Duplex.
“Project・V150”
Breaking new ground at 150 meters per second and 540 km/h
In 2007, a special TGV POS (V150 formation) was used to undertake the world speed record challenge known as “Project V150.” On April 3rd of the same year, it set an astonishing world record of 574.8 km/h, far exceeding the target. This record still stands as the fastest ever for steel-wheel-on-steel-rail trains, proudly holding the title of the world’s fastest.
(The locomotive used for testing was later operated as POS set 4402, and is currently in service as a TGV P-Duplex.)




Extra!
TGV Lesson 2:
“Digging Deeper: The Transformation of the TGV Brand”
Even after more than 40 years since its launch, the TGV continues to evolve with the times. This evolution is not limited to the trains themselves; the “TGV” brand itself has also undergone changes. Today, the service has been differentiated into two brands, “TGV inOui” and “Ouigo,” each tailored to meet specific passenger needs.
2017~
TGV inOui

The TGV inOui was launched in 2017 as a new TGV brand. The train cars retain many of the original features from when the TGV first began operations, including first-class cars and buffet cars.

2013~
Ouigo

Ouigo is an affordable TGV brand that began operations in 2013. It eliminates features such as first-class cars and is designed to be more simplified than traditional TGV services. In 2021, operations also began in Spain under the name “OUIGO España.”

The Next Wave: "The TGV of the Future"
TGV M
In 2023, a new TGV was unveiled for the next generation. The train belongs to the “Avelia” series developed by French manufacturer Alstom and has been named Avelia Horizon. SNCF refers to it as “TGV M,” and it is scheduled to begin service in 2026 as the successor to the TGV-D series.
Compared to previous TGV models, it features improved transport and energy efficiency. The interior design is being handled by the Japanese design firm nendo, led by Oki Sato, bringing new elements never seen before in a TGV. It truly represents the “TGV of the future.”

Manufactured:2023~
The Expansion of the International
High-Speed Rail Network
As demand for the TGV grew, the trains themselves continued to evolve. At the same time, the network expanded across Europe, rapidly developing into an international high-speed rail system that crossed national borders.
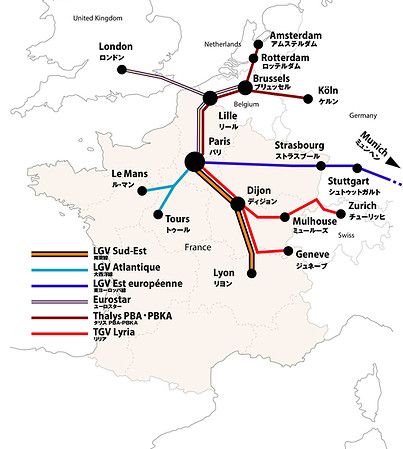
Major Routes of the TGV and International Rail Network (Partial Excerpt Shown in the Map)

1996~2023
Former: Thalys
Current: Eurostar Red
Thalys succeeded the iconic TEE flagship train, the Étoile du Nord, connecting Paris in France, Brussels in Belgium, and Amsterdam in the Netherlands. This service was launched through joint investment by the national railways of each country. Its striking wine-red body became its hallmark.
The R-type locomotives were called Thalys PBA, while the POS-type locomotives—serving an extended route including Cologne (Köln), Germany—were known as PBKA. In 2023, Thalys was merged into Eurostar, and the service was renamed Eurostar RED.

1994~
Eurostar
The Eurostar was introduced in 1994, coinciding with the opening of the Channel Tunnel. Connecting major cities in the UK and France—previously accessible only by air travel—it operates at a top speed of 300 km/h, contributing significantly to the development of the high-speed rail network. The Class 373 trainsets used are based on the TGV design.

2002~
TGV Lyria
In 1993, the French National Railway Company (SNCF) and the Swiss Federal Railways (SBB) established a joint company. After operating under several brand names, “Lyria” was officially established as the brand name in 2002. Initially running single-level trainsets, it now primarily operates as the double-decker Lyria Duplex.
All rights reserved. 1998-2024 株式会社カトー / 株式会社関水金属
★ コンテンツ・写真等の無断転載を禁じます ★



